nLab geometry of physics -- superalgebra
this entry is the first section of “supergeometry and superphysics?”,
which itself is one chapter of “geometry of physics”
next section: supergeometry
previous chapter: categories and toposes
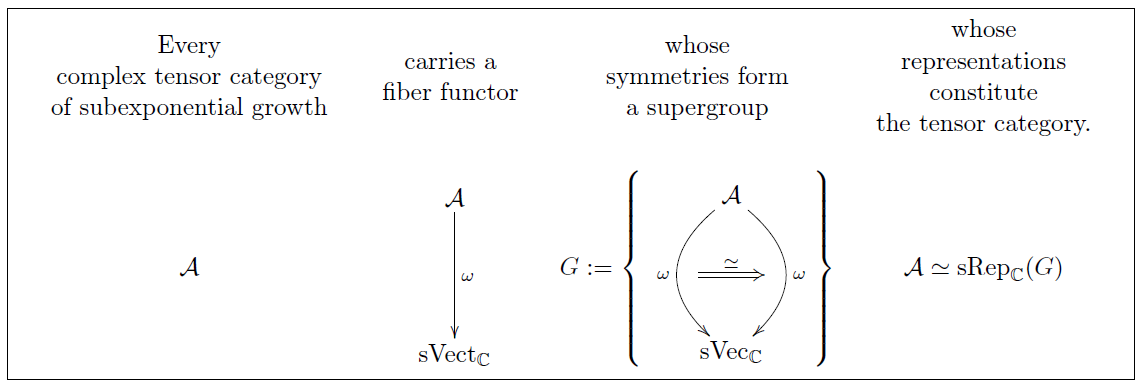
In Klein geometry and Cartan geometry the fundamental geometric concept is the symmetry group of the local model space, which is then recovered as some coset space . These symmetry groups are reflected in their categories of representations , which are certain nice tensor categories. In terms of physics via Wigner classification, the irreducible objects in label the possible fundamental particle species on the spacetime . Hence if we regard the tensor category as the actual fundamental concept, then the natural question is that of Tannaka reconstruction: Given any nice tensor category, is it equivalent to for some symmetry group ? For rigid tensor categories in characteristic zero subject only to a mild size constraint this is answered by Deligne's theorem on tensor categories (theorem below): all of them are, but only if we allow to be a “supergroup”.
Superalgebra
- Tensor products and Super vector spaces
- Commutative algebra in tensor categories and Affine super-spaces
- Monoids in monoidal categories and Supercommutative superalgebra
- Example: Super Lie algebras and Super -algebras
- -Graded Supercommutative superalgebra
- Affine superschemes
- Modules in tensor categories and Super vector bundles
- Super-Groups as super-commutative Hopf algebras
- Linear super-representations as Comodules
- Super Fiber functors and their automorphism supergroups
- Super-exterior powers and Schur functors
- Tannaka duality between tensor categories and supergroups
- References
The beauty of supercommutative superalgebra (Def. below) is that it is just commutative algebra “internal” to the tensor category of super vector spaces. (See the chapter on categories and toposes for the basic concepts of categories and monoidal categories). For instance an (affine algebraic) supergroup (i.e. a super symmetry-group, i.e. a super-symmetry group) is just a commutative Hopf algebra internal to super vector spaces. The beauty of super vector spaces, in turn, is that these are just -graded vector spaces equipped with the unique non-trivial symmetric braiding. Better yet, all tensor categories subject to a mild size constraint are equivalently categories of representations of supergroups. This is the main theorem of this section, theorem below (Deligne's theorem on tensor categories).
Here we introduce and explain all this.
We start by introducing the basic concepts of tensor categories along with the basic examples of vector spaces and super vector spaces:
This allows to speak of commutative algebra internal to tensor categories. Specializing this to the tensor category of super vector spaces yields supercommutative superalgebras. The formal duals of these are the affine super schemes. This we discuss in
In the same dual spirit, super vector bundles over affine super schemes are algebraically incarnated as (finitely generated projctive) modules over supercommutative superalgebras. This we discuss in
Next we introduce the concept of commutative monoids equipped with the structure of a commutative Hopf algebras and explain how these are formal duals to groups. Then we use this to motivate and explain the concept of (affine algebraic) supergroups as formal duals to commutative Hopf algebras internal to the tensor category of super vector spaces, namely supercommutative Hopf algebras:
Then we discuss how under this relationo, then linear representations of groups correspond to comodules over their formally dual commutative Hopf algebras, and we introduce the key class of categories of interest here: tensor-categories of representations of groups and of super-representations of super-groups:
All such categories of representations carry a fiber functor: the forgetful functor that sends any representation to its underlying representation space. Simple as this is, fiber functors turn out to be the key concept in representation theory. Notably, every abstractly defined super fiber functor gives rise to an affine algebraic supergroup, namely its automorphism group. We introduce the basics in
And in fact, under mild conditions this supergorup of automorphisms of the fiber functor of a tensor category is such that the tensor category is equivalently its category of representations. This statement of Tannaka duality for complex-linear tensor categories, due to Pierre Deligne gives superalgebra a general abstract raison d’être. We state the theorem and give some broad indication as to how the proof proceeds in the last sub-section
Tensor products and Super vector spaces
Definition
For a field, we write Vect for the category (this Def.) whose
-
objects are -vector spaces;
-
morphisms are -linear functions between these.
When the ground field is understood or when its precise nature is irrelevant, we will often notationally suppress it and speak of just the category Vect of vector spaces.
This is the category inside which linear algebra takes place.
Of course the category Vect has some special properties. Not only are its objects “linear spaces”, but the whole category inherits linear structure of sorts. This is traditionally captured by the following terminology for additive and abelian categories. Notice that there are several different but equivalent ways to state the following properties (discussed behind the relevant links).
Definition
Let be a category (this Def.).
-
Say that has direct sums if it has finite products and finite coproducts and if the canonical comparison morphism between these is an isomorphism. We write for the direct sum of two objects of .
-
Say that is an additive category if it has direct sums and in addition it is enriched in abelian groups, meaning that every hom-set is equipped with the structure of an abelian group such that composition of morphisms is a bilinear map.
-
Say that is an abelian category if it is an additive category and has property that its monomorphisms are precisely the inclusions of kernels and its epimorphisms are precisely the projections onto cokernels.
We also make the following definition of -linear category, but notice that conventions differ as to which extra properties beyond Vect-enrichment to require on a linear category:
Definition
For a field (or more generally just a commutative ring), call a category a -linear category if
-
it is an abelian category (def. );
-
its hom-sets have the structure of -vector spaces (generally -modules) such that composition of morphisms in is a bilinear map
and the underlying additive abelian group structure of these hom-spaces is that of the underlying abelian category.
In other words, a -linear category is an abelian category with the additional structure of a Vect-enriched category (generally Mod-enriched) such that the underlying Ab-enrichment according to def. is obtained from the -enrichment under the forgetful functor .
A functor between -linear categories is called a -linear functor if its component functions on hom-sets are linear maps with respect to the given -linear structure, hence if it is a Vect-enriched functor.
Example
The category Vect of vector spaces (def. ) is a -linear category according to def. .
Here the abstract direct sum is the usual direct sum of vector spaces, whence the name of the general concept.
For two -vector spaces, the vector space structure on the hom-set of linear maps is given by “pointwise” multiplication and addition of functions:
for all and .
Recall the basic construction of the tensor product of vector spaces:
Definition
Given two vector spaces over some field , , their tensor product of vector spaces is the vector space denoted
whose elements are equivalence classes of tuples of elements with , for the equivalence relation given by
More abstractly this means that the tensor product of vector spaces is the vector space characterized by the fact that
-
it receives a bilinear map
(out of the Cartesian product of the underlying sets)
-
any other bilinear map of the form
factors through the above bilinear map via a unique linear map
The existence of the tensor product of vector spaces, def. , equips the category Vect of vector spaces with extra structure, which is a “categorification” of the familiar structure of a semi-group. One also says “monoid” for semi-group and therefore categories equipped with a tensor product operation are also called monoidal categories (this Def.):
Definition
A monoidal category is a category equipped with
-
a functor
out of the product category of with itself, called the tensor product,
-
an object
called the unit object or tensor unit,
-
called the associator,
-
called the left unitor, and a natural isomorphism
called the right unitor,
such that the following two kinds of diagrams commute, for all objects involved:
-
triangle identity:
-
the pentagon identity:
As expected, we have the following basic example:
Example
(monoidal category of vector spaces)
For a field, the category Vect of -vector spaces becomes a monoidal category (def. ) as follows
-
the abstract tensor product is the tensor product of vector spaces from def. ;
-
the tensor unit is the field itself, regarded as a 1-dimensional vector space over itself;
-
the associator is the map that on representing tuples acts as
-
the left unitor is the map that on representing tuples is given by
and the right unitor is similarly given by
That this satisifes the pentagon identity (def. ) and the left and right unit identities is immediate on representing tuples.
But the point of the abstract definition of monoidal categories is that there are also more exotic examples. The followig one is just a minimal enrichment of example , and yet it will be important.
Example
(monoidal categories of graded vector spaces)
Let be a group (or in fact just a monoid/semi-group). A -graded vector space is a direct sum of vector spaces labeled by the elements in :
of -graded vector spaces is a linear map that respects this direct sum structure, hence equivalently a direct sum of linear maps
for all , such that
This defines a category, denoted . Equip this category with a tensor product which on the underlying vector spaces is just the tensor product of vector spaces from def. , equipped with the -grading which is obtained by multiplying degree labels in :
The tensor unit for the tensor product is the ground field , regarded as being in the degree of the neutral element
The associator and unitors are just those of the monoidal structure on plain vector spaces, from example .
One advantage of abstracting the concept of a monoidal category is that it allows to prove general statements uniformly for all kinds of tensor products, familar ones and more exotic ones. The following lemma and remark are two important such statements.
Lemma
(Kelly 64)
Let be a monoidal category, def. . Then the left and right unitors and satisfy the following conditions:
-
;
-
for all objects the following diagrams commutes:
and
For proof see at monoidal category this lemma and this lemma.
Remark
Just as for an associative algebra it is sufficient to demand and and in order to have that expressions of arbitrary length may be re-bracketed at will, so there is a coherence theorem for monoidal categories which states that all ways of freely composing the unitors and associators in a monoidal category (def. ) to go from one expression to another will coincide. Accordingly, much as one may drop the notation for the bracketing in an associative algebra altogether, so one may, with due care, reason about monoidal categories without always making all unitors and associators explicit.
(Here the qualifier “freely” means informally that we must not use any non-formal identification between objects, and formally it means that the diagram in question must be in the image of a strong monoidal functor from a free monoidal category. For example if in a particular monoidal category it so happens that the object is actually equal to , then the various ways of going from one expression to another using only associators and this “accidental” equality no longer need to coincide.)
The above discussion makes it clear that a monoidal category is like a monoid/semi-group, but “categorified”. Accordingly we may consider additional properties of monoids/semi-groups and correspondingly lift them to monoidal categories. A key such property is commutativity. But while for a monoid commutativity is just an extra property, for a monoidal category it involves choices of commutativity-isomorphisms and hence is extra structure. We will see below that this is the very source of superalgebra.
The categorification of “commutativity” comes in two stages: braiding and symmetric braiding (this Def. and this Def.).
Definition
A braided monoidal category, is a monoidal category (def. ) equipped with a natural isomorphism
(for all objects ) called the braiding, such that the following two kinds of diagrams commute for all objects involved (“hexagon identities”):
and
where denotes the components of the associator of .
Definition
A symmetric monoidal category is a braided monoidal category (def. ) for which the braiding
satisfies the condition:
for all objects
Remark
In analogy to the coherence theorem for monoidal categories (remark ) there is a coherence theorem for symmetric monoidal categories (def. ), saying that every diagram built freely (see remark ) from associators, unitors and braidings such that both sides of the diagram correspond to the same permutation of objects, coincide.
Consider the simplest non-trivial special case of -graded vector spaces from example , the case where is the cyclic group of order two.
Example
A -graded vector space is a direct sum of two vector spaces
where we think of as the summand that is graded by the neutral element in , and of as being the summand that is graded by the single non-trivial element.
A homomorphism of -graded vector spaces
is a linear map of the underlying vector spaces that respects the grading, hence equivalently a pair of linear maps
between then summands in even degree and in odd degree, respectively:
The tensor product of -graded vector space is the tensor product of vector spaces of the underlying vector spaces, but with the grading obtained from multiplying the original gradings in . Hence
and
As in example , this definition makes a monoidal category def. .
Proposition
There are, up to braided monoidal equivalence of categories, precisely two choices for a symmetric braiding (def. )
on the monoidal category of -graded vector spaces from def. :
-
the trivial braiding which is the natural linear map given on tuples representing an element in (according to def. ) by
-
the super-braiding which is the natural linear function given on tuples of homogeneous degree (i.e. , for ) by
Proof
For a monoidal category, write
for the full subcategory on those which are invertible objects under the tensor product, i.e. such that there is an object with and . Since the tensor unit is clearly in (with ) and since with also (with ) the monoidal category structure on restricts to .
Accordingly any braiding on restricts to a braiding on . Hence it is sufficient to show that there is an essentially unique non-trivial symmetric braiding on , and that this is the restriction of a braiding on .
Now is necessarily a groupoid (the “Picard groupoid” of ) and in fact is what is called a 2-group. As such we may regard it equivalently as a homotopy 1-type with group structure, and as such it it is equivalent to its delooping
regarded as a pointed homotopy type. (See at looping and delooping).
The Grothendieck group of is
the fundamental group of the delooping space.
Now a symmetric braiding on is precisely the structure that makes it a symmetric 2-group which is equivalently the structure of a second delooping (for the braiding) and then a third delooping (for the symmetry), regarded as a pointed homotopy type.
This way we have rephrased the question equivalently as a question about the possible k-invariants of spaces of this form.
Now in the case at hand, has precisely two isomorphism classes of objects, namely the ground field itself, regarded as being in even degree and regarded as being in odd degree. We write and for these, respectively. By the rules of the tensor product of graded vector spaces we have
and
In other words
Now under the above homotopical identification the non-trivial braiding is identified with the elements
Due to the symmetry condition (def. ) we have
which implies that
Therefore for classifying just the symmetric braidings, it is sufficient to restrict the hom-spaces in from being either or empty, to hom-sets being or empty. Write for the resulting 2-group.
In conclusion then the equivalence classes of possible k-invariants of , hence the possible symmetric braiding on are in the degree-4 ordinary cohomology of the Eilenberg-MacLane space with coefficients in . One finds (…)
Definition
The symmetric monoidal category (def. )
-
whose underlying monoidal category is that of -graded vector spaces (example );
-
whose braiding (def. ) is the unique non-trivial symmtric grading from prop. is called the category of super vector spaces
Remark
The non-full symmetric monoidal subcategory
of
(on the two objects and and with hom-sets restricted to , as in the proof of prop. ) happens to be the 1-truncation of the looping of the sphere spectrum , regarded as a group-like E-infinity space (“abelian infinity-group”)
It has been suggested (in Kapranov 15) that this and other phenomena are evidence that in the wider context of homotopy theory/stable homotopy theory super-grading (and hence superalgebra) is to be regarded as but a shadow of grading in higher algebra over the sphere spectrum. Notice that the sphere spectrum is just the analog of the group of integers in stable homotopy theory.
The following is evident but important
Proposition
The canonical inclusion
of the category of vector spaces (def. ) into that of super vector spaces (def. ) given by regarding a vector space as a super-vector space concentrated in even degree, extends to a braided monoidal functor (def. ).
Definition
Given a symmetric monoidal category with tensor product (def. ) it is called a closed monoidal category if for each the functor has a right adjoint, denoted
hence if there are natural bijections
for all objects .
Since for the case that is the tensor unit of this means that
the object is an enhancement of the ordinary hom-set to an object in . Accordingly, it is also called the internal hom between and .
In a closed monoidal category, the adjunction isomorphism between tensor product and internal hom even holds internally:
Proposition
In a symmetric closed monoidal category (def. ) there are natural isomorphisms
whose image under are the defining natural bijections of def. .
Proof
Let be any object. By applying the defining natural bijections twice, there are composite natural bijections
Since this holds for all , the Yoneda lemma (the fully faithfulness of the Yoneda embedding) says that there is an isomorphism . Moreover, by taking in the above and using the left unitor isomorphisms and we get a commuting diagram
Definition
Let and be two (pointed) topologically enriched monoidal categories (def. ). A lax monoidal functor between them is
satisfying the following conditions:
-
(associativity) For all objects the following diagram commutes
where and denote the associators of the monoidal categories;
-
(unitality) For all the following diagrams commutes
and
where , , , denote the left and right unitors of the two monoidal categories, respectively.
If and all are isomorphisms, then is called a strong monoidal functor.
If moreover and are equipped with the structure of braided monoidal categories (def. ) with braidings and , respectively, then the lax monoidal functor is called a braided monoidal functor if in addition the following diagram commutes for all objects
A homomorphism between two (braided) lax monoidal functors is a monoidal natural transformation, in that it is a natural transformation of the underlying functors
compatible with the product and the unit in that the following diagrams commute for all objects :
and
We write for the resulting category of lax monoidal functors between monoidal categories and , similarly for the category of braided monoidal functors between braided monoidal categories, and for the category of braided monoidal functors between symmetric monoidal categories.
Remark
In the literature the term “monoidal functor” often refers by default to what in def. is called a strong monoidal functor.
If and are symmetric monoidal categories (def. ) then a braided monoidal functor (def. ) between them is often called a symmetric monoidal functor.
Example
Let be the symmetric monoidal category of -graded vector spaces (example ) or of super vector spaces (example ). Then there is an evident forgetful functor
to the category of plain vector spaces, which forgets the grading.
In both cases this is a strong monoidal functor (def. ) For it is also a braided monoidal functor, but for it is not.
Proposition
For two composable lax monoidal functors (def. ) between monoidal categories, then their composite becomes a lax monoidal functor with structure morphisms
and
We now discuss one more extra property on monoidal categories
Definition
Let be a monoidal category (def. )
Then right duality between objects
consists of
-
a morphism of the form
called the counit of the duality, or the evaluation map;
-
a morphism of the form
called the unit or coevaluation map
such that
-
(triangle identity) the following diagrams commute
and
where denotes the associator of the monoidal category , and and denote the left and right unitors, respectively.
We say that is the right dual object to . Similarly a left dual for is an object and the structure of as a right dual of . If is equipped with the structure of a braided monoidal category, then every right dual is canonically also a left dual.
If in a monoidal category every object has a left and right dual, then it is called a rigid monoidal category.
Example
Let
be the full subcategory FinDimVect of that of all vector spaces (over the given ground field ) on those which are finite dimensional vector spaces.
Clearly the tensor product of vector spaces (def. ) restricts to those of finite dimension, and so there is the induced monoidal category structure from example
This is a a rigid monoidal category (def. ) in that for any finite dimensional vector spaces, its ordinary linear dual vector space
is a dual object in the abstract sense of def. .
Here the evaluation map is literally the defining evaluation map of linear duals (whence the name of the abstract concept)
The co-evaluation map
is the linear map that sends to under the canonical identification of with the linear space of linear endomorphisms of .
If we choose a linear basis for and a corresponding dual bases of , then the evaluation map is given by
(with the Kronecker delta on the right) and the co-evaluation map is given by
In this perspective the triangle identities are the statements that
and
Physicists will recognize this as just the basic rules for tensor calculus in index-notation.
Example
Similarly, the full subcategory
of the symmetric monoidal category of super vector spaces from example , on those of finite total dimension is a rigid monoidal category.
Here we say that a super vector space has dimension
if its even part has dimension and its odd part has dimension :
The dual object of such a finite dimensional super vector space is just the linear dual vector space as in example , equipped with the evident grading:
Proposition
Every rigid (def. \refDualizableObject) symmetric monoidal category (def. ) is a closed monoidal category (def. ) with internal hom between two objects given by the tensor product of the codomain object with the dual object of the domain object
(The closed monoidal categories arising this way are called compact closed categories).
Proof
The natural isomorphism that characterizes the internal hom as being right adjoint to the tensor product is given by the adjunction natural isomorphism that characterizes dual objects:
There are many monoidal categories whose “tensor product” operation is quite unlike the tensor product of vector spaces. Hence one says tensor category for monoidal categories that are also -linear categories and such that the tensor product functor suitably reflects that linear structure. There are slight variants of what people mean by a “tensor category”. Here we mean precisely the following:
Definition
For a field, then a -tensor category is an
-
k-linear (def. )
-
rigid (def. )
-
symmetric (def. )
-
monoidal category (def. )
such that
-
the tensor product functor is in both arguments separately
-
(the endomorphism ring of the tensor unit coincides with ).
In this form this is considered in (Deligne 02, 0.1).
We consider now various types of size constraints on tensor categories. The Tannaka reconstruction theorem (theorem below) only assumes one of them (subexponential growth, def. ), but the others appear in the course of the proof of the theorem.
Recall the concept of length of an object in an abelian category, a generalization of the concept of dimension of a free module/vector space.
Definition
Let be an abelian category. Given an object , then a Jordan-Hölder sequence or composition series for is a finite filtration, i.e. a finite sequence of subobject unclusions into , starting with the zero objects
such that at each stage the quotient (i.e. the coimage of the monomorphism ) is a simple object of .
If a Jordan-Hölder sequence for exists at all, then is said to be of finite length.
(e.g. EGNO 15, def. 1.5.3)
Proposition
If has finite length according to def. , then in fact all Jordan-Hölder sequences for have the same length .
(e.g. EGNO 15, theorem 1.5.4)
Definition
If an object has finite length according to def. , then the length of any of its Jordan-Hölder sequences, which is uniquely defined according to prop. , is called the length of the object .
(e.g. EGNO 15, def. 1.5.5)
Definition
A -tensor category (def. ) is called finite (over ) if
-
There are only finitely many simple objects in (hence it is a finite abelian category), and each of them admits a projective presentation.
-
Each object is of finite length;
-
For any two objects , of , the hom-object (-vector space) has finite dimension;
Example
The category of finite dimensional vector spaces over is a finite tensor category according to def. . It has a single isomorphism class of simple objects, namely itself.
Also category of finite dimensional super vector spaces is a finite tensor category. This has two isomorphism classes of simple objects, regarded in even degree, and regarded in odd degree.
The following finiteness condition is useful in the proof of the main theorem, but not necessary for its statement (according to Deligne 02, bottom of p. 3):
Definition
A -tensor category (def. ) is called finitely -generated if there exists an object such that every other object is a subquotient of a direct sum of tensor products , for some :
Such is called an -generator for .
The following is the main size constraint needed in the theorem. Notice that it is a “mild” constraint at least in the intuitive sense that it states just a minimum assumption on the expected behaviour of dimension (length) under tensor powers.
Definition
A tensor category (def. ) is said to have subexponential growth* if the length of tensor exponentials is no larger than the exponential of the length: for every object there exists a natural number such that is of length at most , and that also all tensor product powers of are of length bounded by the corresponding powers of :
(e.g. EGNO 15, def. 9.11.1)
The evident example is the following:
Example
The tensor category -FinDimVect of finite dimensional vector spaces from example has subexponential growth (def. ), for the dimension of a vector space , we have
While many linear monoidal categories of interest do not satisfy finiteness or rigidity (def. ), often they are such that all their objects are (formal) inductive limits over “small” objects that do form a rigid monoidal category.
Proposition
Let a tensor category (def. ), such that
-
all hom spaces are of finite dimension over
then for its category of ind-objects the following holds
-
is an abelian category
-
is a full subcategory
-
which stable under forming subquotients
-
such that that every object is the filtered colimit of those of its subobjects that are in ;
-
-
inherits a tensor product by
where , by the above.
-
satisfies all the axioms of def. except that it fails to be essentially small and rigid category. In detail
- an object in is dualizable precisely if it is in .
Example
The category of all vector spaces is the category of ind-objects of the tensor category of finite dimensional vector spaces (example ):
Similarly the category of all super vector spaces (def. ) is the category of ind-objects of that of finite-dimensional super vector spaces (example )
Commutative algebra in tensor categories and Affine super-spaces
The key idea of supercommutative superalgebra is that it is nothing but plain commutative algebra but “internalized” not in ordinary vector spaces, but in super vector spaces. This is made precise by def. and def. below.
The key idea then of supergeometry is to define super-spaces to be spaces whose algebras of functions are supercommutative superalgebras. This is not the case for any “ordinary” space such as a topological space or a smooth manifold. But these spaces may be characterized dually via their algebras of functions, and hence it makes sense to generalize the latter.
For smooth manifolds the duality statement is the following:
Proposition
(embedding of smooth manifolds into formal duals of R-algebras)
The functor
which sends a smooth manifold (finite dimensional, paracompact, second countable) to (the formal dual of) its -algebra of smooth functions is a full and faithful functor.
In other words, for two smooth manifolds there is a natural bijection between the smooth functions and the -algebra homomorphisms .
A proof is for instance in (Kolar-Slovak-Michor 93, lemma 35.8, corollaries 35.9, 35.10).
This says that we may identify smooth manifolds as the “formal duals” of certain associative algebras, namely those in the image of the above full embedding. Accordingly then, any larger class of associative algebras than this may be thought of as the class of formal duals to a generalized kind of manifold, defined thereby. Given any associative algebra , then we may think of it as representing a space which is such that it has as its algebra of functions.
This duality between certain spaces and their algebras of functions is profound. In physics it has always been used implicitly, in fact it was so ingrained into theoretical physics that it took much effort to abstract away from coordinate functions to discover global Riemannian geometry in the guise of “general relativity”. As mathematics, an early prominent duality theorem is Gelfand duality (between topological spaces and C*-algebras) which served as motivation for the very definition of algebraic geometry, where affine schemes are nothing but the formal duals of commutative rings/commutative algebras. Passing to non-commutative algebras here yields non-commutative geometry, and so forth. In great generality this duality between spaces and their function algebras appears as “Isbell duality” between presheaves and copresheaves.
In supergeometry we are concerned with spaces that are formally dual to associative algebras which are “very mildly” non-commutative, namely supercommutative superalgebras. These are in fact commutative algebras when viewed internal to super vector spaces (def. below). The corresponding formal dual spaces are, depending on some technical details, super schemes or supermanifolds. In the physics literature, such spaces are usually just called superspaces.
We now make this precise.
Monoids in monoidal categories and Supercommutative superalgebra
Definition
Given a monoidal category (def ), then a monoid internal to is
such that
-
(associativity) the following diagram commutes
where is the associator isomorphism of ;
-
(unitality) the following diagram commutes:
where and are the left and right unitor isomorphisms of .
Moreover, if has the structure of a symmetric monoidal category (def. ) with symmetric braiding , then a monoid as above is called a commutative monoid in if in addition
-
(commutativity) the following diagram commutes
A homomorphism of monoids is a morphism
in , such that the following two diagrams commute
and
Write for the category of monoids in , and for its subcategory of commutative monoids.
Example
A monoid object according to def. in the monoidal category of vector spaces from example is equivalently an ordinary associative algebra over the given ground field. Similarly a commutative monoid in is an ordinary commutative algebra. Moreover, in both cases the homomorphisms of monoids agree with usual algebra homomorphisms. Hence there are equivalences of categories.
Example
For a group, then a -graded associative algebra is a monoid object according to def. in the monoidal category of -graded vector spaces from example .
This means that a -graded algebra is
-
an associative algebra structure on the underlying vector space
such that for two elements of homogeneous degree, i.e. and then their product is in degree
Example motivates the following definition:
Definition
(supercommutative superalgebra)
A supercommutative superalgebra is a commutative monoid (def. ) in the symmetric monoidal category of super vector spaces (def. ). We write for the category of supercommutative superalgebras with the induced homomorphisms between them:
Unwinding what this means, then a supercommutative superalgebra is
Remark
In view of def. we might define a not-necessarily supercommutative superalgebra to be a monoid (not necessarily commutative) in sVect, and write
However, since the definition of not-necessarily commutative monoids (def. ) does not invoke the braiding of the ambient tensor category, and since super vector spaces differ from -graded vector spaces only via their braiding (example ), this yields equivalently just the -graded algebras from example :
Hence the heart of superalgebra is super-commutativity.
Example
The supercommutative superalgebra which is freely generated over from generators in odd degree is the quotient of the tensor algebra , with the generators in odd degree, by the ideal generated by the relations
for all .
This is also called a Grassmann algebra, in honor of (Grassmann 1844), who introduced and studied the super-sign rule in def. a century ahead of his time.
We also denote this algebra by
The following is an elementary but fundamental fact about the relation between commutative algebra and supercommutative superalgebra. It is implicit in much of the literature, but maybe the only place where it has been made explicit before is (Carchedi-Roytenberg 12, example 3.18).
Proposition
There is a full subcategory inclusion
of commutative algebras (example ) into supercommutative superalgebras (def. ) induced via prop. from the full inclusion
of vector spaces (def. ) into super vector spaces (def. ), which is a braided monoidal functor by prop. . Hence this regards a commutative algebra as a superalgebra concentrated in even degree.
This inclusion functor has both a left adjoint functor and a right adjoint functor , (an adjoint triple exibiting a reflective subcategory and coreflective subcategory inclusion, an “adjoint cylinder”):
Here
-
the right adjoint sends a supercommutative superalgebra to its even part ;
-
the left adjoint sends a supercommutative superalgebra to the quotient by the ideal which is generated by its odd part (hence it sets all elements to zero which may be written as a product such that at least one factor is odd-graded).
Proof
The full inclusion is evident. To see the adjunctions observe their characteristic natural bijections between hom-sets: If is an ordinary commutative algebra regarded as a superalgebra concentrated in even degree, and if is any superalgebra,
-
then every super-algebra homomorphism of the form must factor through , simply because super-algebra homomorpism by definition respect the -grading. This gives a natural bijection
-
every super-algebra homomorphism of the form must send every odd element of to 0, again because homomorphisms have to respect the -grading, and since homomorphisms of course also preserve products, this means that the entire ideal generated by must be sent to zero, hence the homomorphism must factor through the projection , which gives a natural bijection
Example: Super Lie algebras and Super -algebras
As an example of the general principle of internalizing ordinary algebra in super vector spaces in order to obtain the analogous concept in superalgebra, we consider the concepts of super Lie algebras and of super L-∞ algebras (super Lie n-algebras for arbitrary ).
Definition
A super Lie algebra is a Lie algebra object internal to the symmetric monoidal category of super vector spaces (def. ). Hence this is
-
a homomorphism
of super vector spaces (the super Lie bracket)
such that
-
the bracket is skew-symmetric in that the following diagram commutes
(here is the braiding natural isomorphism in the category of super vector spaces)
-
the Jacobi identity holds in that the following diagram commutes
Externally this means the following:
Proposition
A super Lie algebra according to def. is equivalently
-
a -graded vector space ;
-
equipped with a bilinear map (the super Lie bracket)
which is graded skew-symmetric: for two elements of homogeneous degree , , respectively, then
-
that satisfies the -graded Jacobi identity in that for any three elements of homogeneous super-degree then
A homomorphism of super Lie algebras is a homomorphisms of the underlying super vector spaces which preserves the Lie bracket. We write
for the resulting category of super Lie algebras.
Definition
For a super Lie algebra of finite dimension, then its Chevalley-Eilenberg algebra is the super-Grassmann algebra on the dual super vector space
equipped with a differential that on generators is the linear dual of the super Lie bracket
and which is extended to by the graded Leibniz rule (i.e. as a graded derivation).
Here all elements are -bigraded, the first being the cohomological grading in , the second being the super-grading (even/odd).
For two elements of homogeneous bi-degree , respectively, the sign rule is
(See at signs in supergeometry for discussion of this sign rule and of an alternative sign rule that is also in use. )
We may think of equivalently as the dg-algebra of left-invariant super differential forms on the corresponding simply connected super Lie group .
The concept of Chevalley-Eilenberg algebras is traditionally introduced as a means to define Lie algebra cohomology:
Definition
Given a super Lie algebra , then
-
an -cocycle on (with coefficients in ) is an element of degree in its Chevalley-Eilenberg algebra (def. ) which is closed.
-
the cocycle is non-trivial if it is not -exact
-
hene the super-Lie algebra cohomology of (with coefficients in ) is the cochain cohomology of its Chevalley-Eilenberg algebra
The following says that the Chevalley-Eilenberg algebra is an equivalent incarnation of the super Lie algebra:
Proposition
The functor
that sends a finite dimensional super Lie algebra to its Chevalley-Eilenberg algebra (def. ) is a fully faithful functor which hence exibits super Lie algebras as a full subcategory of the opposite category of differential-graded algebras.
This makes it immediate how to generalize to super L-infinity algebras:
Definition
A super L-∞ algebra is an L-∞ algebra internal to the symmetric monoidal category of super vector spaces (def. ).
Explicitly this means the following:
Definition
(super graded signature of a permutation)
Let be a -graded super vector space, hence a -bigraded vector space.
For let
be an n-tuple of elements of of homogeneous degree , i.e. such that .
For a permutation of elements, write for the signature of the permutation, which is by definition equal to if is the composite of permutations that each exchange precisely one pair of neighboring elements.
We say that the super -graded signature of
is the product of the signature of the permutation with a factor of
for each interchange of neighbours to involved in the decomposition of the permuation as a sequence of swapping neighbour pairs (see at signs in supergeometry for discussion of this combination of super-grading and homological grading).
Now def. is equivalent to the following def. . This is just the definiton for L-infinity algebras, with the pertinent sign now given by def. .
Definition
An super L-∞ algebra is
-
a -graded vector space ;
-
for each a multilinear map, called the -ary bracket, of the form
and of degree
such that the following conditions hold:
-
(super graded skew symmetry) each is graded antisymmetric, in that for every permutation of elements and for every n-tuple of homogeneously graded elements then
where is the super -graded signature of the permuation , according to def. ;
-
(strong homotopy Jacobi identity) for all , and for all (n+1)-tuples of homogeneously graded elements the followig equation holds
(1)where the inner sum runs over all -unshuffles and where is the super graded signature sign from def. .
A strict homomorphism of super -algebras
is a linear map that preserves the bidegree and all the brackets, in an evident sens.
A strong homotopy homomorphism (“sh map”) of super -algebras is something weaker than that, best defined in formal duals, below in def. .
Definition
A super algebra is of finite type if the underlying -graded vector space is degreewise of finite dimension.
If is of finite type, then its Chevalley-Eilenberg algebra is the dg-algebra whose underlying graded algebra is the super-Grassmann algebra
of the graded degreewise dual vector space , equipped with the differential which on generators is the sum of the dual linear maps of the -ary brackets:
and extended to all of as a super-graded derivation of degree .
Notice that here the signs in supergeometry are such that for elements of homogenous bidegree, then
and
(see at signs in supergeometry for more on this).
A strong homotopy homomorphism (“sh-map”) between super -algbras of finite type
is defined to be a homomorphism of dg-algebras between their Chevalley-Eilenberg algebras going the other way:
(here is the primitive concept, and is defined as the formal dual of ). Hence the category of super -algebras of finite type is the full subcategory
of the opposite category of dg-algebras on those that are CE-algebras as above.
Finally, the cochain cohomology of the Chevalley-Eilenberg algebra of a super algebra of finite type is its L-∞ algebra cohomology with coefficients in :
Remark
In their formal dual incarnations as super-graded commutative dg-algebras, i.e. super Chevalley-Eilenberg algebras (def. ), super L-∞ algebras of finite type had secretly been introduced within the supergravity literature already in D’Auria-Fré-Regge 80 and explicitly in van Nieuwenhuizen 82 and hence a whole decade before mathematicans considered even plain (non-super) L-∞ algebras (in Lada-Stasheff 92).
The concept was picked up in the D'Auria-Fré formulation of supergravity (D’Auria-Fré 82) and eventually came to be referred to as “FDA”s (short for “free differential algebra”) in the supergravity literature, where in rational homotopy theory one says “semifree dga” or “quasifree dga”, since these dg-algebras are crucially not required to be free as differential algebras). (If they are, then they are Weil algebras).
The relation between super -algebras and the “FDA”s of the supergravity literature is made explicit in (FSS 13).
-Graded Supercommutative superalgebra
It may happen that the -grading of a supercommutative superalgebra lifts to a finer grading with respect to some abelian group , through a group homomorphism . The most important special case of this is the lift to -grading through the mod-2-reduction . We discuss how the resulting -graded-commutative algebra is related to -graded-commutative algebra, i.e. supercommutative superalgebra.
This relation is particularly interesting since there is a natural source of -graded-commutative algebra: the commutative monoids in homological algebra (called dgca-s) and more generally in stable homotopy theory (called homotopy commutative ring spectra) have shadows on chain homology/homotopy groups which are -graded-commutative algebras.
Definition
Write
for the symmetric monoidal category whose underlying monoidal category is that of -graded vector spaces (example ) (for the additive group of integers) equipped with the symmetric braiding which is that of the underlying super vector space (def. ) under the mod-2 reduction of grading .
This means that for two -graded vector spaces then
is the linear map given on representatives elements and of homogeneous degree by
Remark
Beware that there is also the concept of -graded objects internal to the category of super vector spaces. This is not equivalent to the concept in def. .
Example
The category of commutative monoids (def. ) in the category of -graded super vector spaces in the sense of def.
is equivalently the full subcategory of associative algebras over on those algebras which are supercommutative superalgebras (def. ) whose -grading is lifted to a -grading through . Equivalently these are the -graded algebras over such that any two elements of homogeneous degree the product satisfies
These are often called -graded commutative algebras.
Of course analogous definitions apply for the ground field replaced by any ground ring.
One reason why example is of interest is that commutative algebras in homological algebra and in stable homotopy theory give examples:
Example
The category of chain complexes becomes a closed symmetric monoidal category (def. , def. ) with tensor product of chain complexes given degreewise by the tensor product of underlying -graded vector spaces (example ) and with differential given on elements in homogeneous degree by
See at the chapter on homotopy types the section Categories of chain complexes.
A differential graded-commutative algebra is a commutative monoid in (def. ).
Under passing to chain homology, a differential graded-commutative algebra goes to a -graded commutative algebra in the sense of example :
Example
Given a homotopy commutative ring spectrum (i.e., via the Brown representability theorem, a multiplicative generalized cohomology theory), then its stable homotopy groups inherit the structure of a -graded super-commutative ring as in example .
See at Introduction to Stable homotopy theory in the section 1-2 Homotopy commutative ring spectra this proposition.
The following relation between -grading and -grading is elementary but important. It was highlighted in Rezk 09, section 2:
Proposition
Write
for the -graded-commutative algebra (example ) which is freely generated from a single invertible generator in degree 2:
Then there are strong monoidal functors
which exhibit an equivalence of categories between its categories of modules (def. ) and the category of super vector spaces (def. ).
Here the functor sends a -graded vector space to the -graded vector space .
Proof
It is clear that the functor is essentially surjective. Hence we need to see that it is fully faithful.
Since is multiplicatively invertible, by definition, the module-property implies that for any then the action by and establish linear isomorphisms of the form
for all . Since morphisms in respect the multiplication by , they are uniquely determined by their components and , hence by their image under the given functor, and every choice of components and extends to a mophism . Hence is fully faithful.
This implies that, conversely, plain supercommutative superalgebras arise as -graded supercommutative superalgebra with extra structure:
Proposition
Write again
for the free -graded supercommutative superalgebra on a single invertible generator of even degree from prop. .
Then there is an equivalence of categories between -algebras (def. ) (i.e. objects of equipped with a homomorphism , by prop. ) and plain supercommutative superalgebras (def. )
As before, all these considerations of course work also for replaced by any other ground ring.
Example
Let be an even 2-periodic E-infinity ring, such as MP, KU or the spectrum underlying any elliptic cohomology theory or Morava E-theory. Then its -graded-commutative ring of stable homotopy groups according to example is of the form
with an invertible generator in degree 2 (the complex orientation).
Accordingly, for an E-infinity algebra over , hence an E-infinity ring equipped with an -homomorphism , then its underlying -graded commutative algebra (according to example ) is an algebra over . Hence via prop. is canonically identified with a supercommutative superalgebra over .
This is amplified in Rezk 09, section 2. See at spectral super-scheme for more.
Beware that for this equivalence of categories in prop. the action of the element is crucual. The following proposition shows that it is not sufficient to just consider 2-periodically -graded algebras:
Proposition
There is a pair of adjoint functors
between the categories of supercommutative superalgebras (def. ) and that of -graded supercommutative superalgebras according to def. , where
-
the left adjoint simply forgets the lift to a -grading,
-
the right adjoint sends a supercommutative superalgebra to the periodically -graded algebra with
whose product is elementwise that of , under these identifications;
Here is a faithful functor, but not a full functor.
Proof
It is immediate to check the natural bijection between hom sets that characterizes the adjunction:
For and then a morphism
in
is a homomorphism of the underlying -algebras subject to the constraint that for all then
This constraint is equivalent to
which in turn is equivalently the constraint on an algebra homomorphism to constitute a morphism of the form
This establishes the adjunction.
It is immediate to see by direct inspection that is a faithful functor. More abstractly, from the above one sees that the counit of the adjunction is on a superalgebra given by the morphism
which is componentwise the identity. This is clearly an epimorphism, but not a monomorphism, hence not an isomorphism. By general properties of adjoint functors (this prop.), this means that is a faithful functor but not a full functor.
Affine superschemes
It is useful to make explicit the following formally dual perspective on supercommutative superalgebras:
Definition
For a symmetric monoidal category, then we write
for the opposite category of the category of commutative monoids in , according to def. .
For we write
for the same object, regarded in the opposite category. We also call this the affine scheme of . Conversely, for , we write
for the same object, regarded in the category of commutative monoids. We also call this the algebra of functions on .
Definition
For the special case that sVect (def. ) in def. , then we say that the objects in
are affine super schemes over .
Example
For an ordinary commutative algebra over , then of course this becomes a supercommutative superalgebra by regarding it as being concentrated in even degrees. Accordingly, via def. , ordinary affine schemes fully embed into affine super schemes (def. )
In particular for an ordinary Cartesian space, this becomes an affine superscheme in even degree, under the above embedding. As such, it is usually written
Example
The formal dual space, according to def. (example ) to a Grassmann algebra (example ) is to be thought of as a space which is “so tiny” that the coefficients of the Taylor expansion of any real-valued function on it become “so very small” as to be actually equal to zero, at least after the -th power.
For instance for then a general element of is of the form
for , to be compared with the Taylor expansion of a smooth function , which is of the form
Therefore the formal dual space to a Grassmann algebra behaves like an infinitesimal neighbourhood of a point. Hence these are also called superpoints and one writes
Example
Combining example with example , and using prop. , we obtain the affine super schemes
These may be called the super Cartesian spaces. The play the same role in the theory of supermanifolds as the ordinary Cartesian spaces do for smooth manifolds. See at geometry of physics – supergeometry for more on this.
Definition
Given a supercommutative superalgebra (def. ), its parity involution is the algebra automorphism
which on homogeneously graded elements of degree is multiplication by the degree
(e.g. arXiv:1303.1916, 7.5)
Dually, via def. , this means that every affine super scheme has a canonical involution.
Here are more general and more abstract examples of commutative monoids, which will be useful to make explicit:
Example
Given a monoidal category (def. ), then the tensor unit is a monoid in (def. ) with product given by either the left or right unitor
By lemma , these two morphisms coincide and define an associative product with unit the identity .
If is a symmetric monoidal category (def. ), then this monoid is a commutative monoid.
Example
Given a symmetric monoidal category (def. ), and given two commutative monoids , (def. ), then the tensor product becomes itself a commutative monoid with unit morphism
(where the first isomorphism is, (lemma )) and with product morphism given by
(where we are notationally suppressing the associators and where denotes the braiding of ).
That this definition indeed satisfies associativity and commutativity follows from the corresponding properties of , and from the hexagon identities for the braiding (def. ) and from symmetry of the braiding.
Similarly one checks that for then the unit maps
and the product map
and the braiding
are monoid homomorphisms, with equipped with the above monoid structure.
Monoids are preserved by lax monoidal functors:
Proposition
Let and be two monoidal categories (def. ) and let be a lax monoidal functor (def. ) between them.
Then for a monoid in (def. ), its image becomes a monoid by setting
(where the first morphism is the structure morphism of ) and setting
(where again the first morphism is the corresponding structure morphism of ).
This construction extends to a functor
from the category of monoids of (def. ) to that of .
Moreover, if and are symmetric monoidal categories (def. ) and is a braided monoidal functor (def. ) and is a commutative monoid (def. ) then so is , and this construction extends to a functor
Proof
This follows immediately from combining the associativity and unitality (and symmetry) constraints of with those of .
Modules in tensor categories and Super vector bundles
Above (in def. ) we considered spaces from a dual perspective, as determined by their algebras of functions . In the same spirit then we are to express various constructions on and with spaces in terms of dual algebraic constructions.
A key such construction is that of vector bundles over . Here we discuss the corresponding algebraic incarnation of these, namely as modules over algebras of functions.
Suppose that is a smooth manifold, and is an ordinary smooth real vector bundle over . A section of this vector bundle is a smooth function such that
Write for the set of all such sections. Observe that this set inherits various extra structure.
First of all, since is a vector bundle, we have fiber-wise the vector space operations. This means that given two elements in the real numbers, and given two sections and , we may form in each fiber the linear combination . This hence yields a new section . Hence the set of sections of a vector bundle naturally forms itself a vector space.
But there is more structure. We need not multiply with the same element in each fiber, but we may multiply the section in each fiber by a different element, as long as the choice of element varies smoothly with the fibers, so that the resulting section is still smooth.
In other words, every element in the -algebra of smooth functions on , takes a smooth section of to a new smooth section . This operation enjoys some evident properties. It is bilinear in the real vector spaces and , and it satisfies the “action property”
for any two smooth functions .
One says that a vector space such as equipped with an action of an algebra this way is a module over .
In conclusion, any vector bundle gives rise to an -module of sections.
The smooth Serre-Swan theorem states sufficient conditions on such that the converse holds. Together with the embedding of smooth manifolds into formal duals of R-algebras (prop ), this means that differential geometry is “more algebraic” than it might superficially seem, hence that its “algebraic deformation” to supergeometry is more natura than it might superficially seem:
Proposition
(smooth Serre-Swan theorem, Nestruev 03)
For a smooth manifold, then the construction which sends a smooth vector bundle to its -module of sections is an equivalence of categories
between that of smooth vector bundles of finite rank over and that of finitely generated projective modules over the -algebra of smooth functions on .
One may turn the Serre-Swan theorem around to regard for any commutative monoid in some symmetric monoidal category (def. ), the modules over as “generalized vector bundles” over the space (def. ). These “generalized vector bundles” are called “quasicoherent sheaves” over affines. Specified to the case that sVect, this hence yields a concept of super vector bundles.
We now state the relevant definitions and constructions formally.
Definition
Given a monoidal category (def. ), and given a monoid in (def. ), then a left module object in over is
such that
-
(unitality) the following diagram commutes:
where is the left unitor isomorphism of .
-
(action property) the following diagram commutes
A homomorphism of left -module objects
is a morphism
in , such that the following diagram commutes:
For the resulting category of modules of left -modules in with -module homomorphisms between them, we write
The following degenerate example turns out to be important for the general development of the theory below.
Example
Given a monoidal category (def. ) with the tensor unit regarded as a monoid in a monoidal category via example , then the left unitor
makes every object into a left module, according to def. , over . The action property holds due to lemma . This gives an equivalence of categories
of with the category of modules over its tensor unit.
Example
The classical subject of algebra, not necessarily over ground fields, is the above general concepts of monoids and their modules specialized to the ambient symmetric monoidal category being the category Ab of abelian groups regarded as a symmetric monoidal category via the tensor product of abelian groups (whose tensor unit is the additive group of integers ):
-
A commutative monoid in in (def. ) is equivalently a commutative ring .
-
An -module object in (def. ) is equivalently an -module;
-
The tensor product of -module objects (def. ) is the standard tensor product of modules.
-
The category of module objects (def. ) is the standard category of modules .
Example
Let be a discrete group and write for its group algebra over the ground field . Then -modules in Vect are equivalently linear representations of .
Proposition
In the situation of def. , the monoid canonically becomes a left module over itself by setting . More generally, for any object, then naturally becomes a left -module by setting:
The -modules of this form are called free modules.
The free functor constructing free -modules is left adjoint to the forgetful functor which sends a module to the underlying object .
Proof
A homomorphism out of a free -module is a morphism in of the form
fitting into the diagram (where we are notationally suppressing the associator)
Consider the composite
i.e. the restriction of to the unit “in” . By definition, this fits into a commuting square of the form (where we are now notationally suppressing the associator and the unitor)
Pasting this square onto the top of the previous one yields
where now the left vertical composite is the identity, by the unit law in . This shows that is uniquely determined by via the relation
This natural bijection between and establishes the adjunction.
Definition
Given a closed symmetric monoidal category with braiding denoted (def. , def. ), given a commutative monoid in (def. ), and given and two left -module objects (def.), then
-
the tensor product of modules is, if it exists, the coequalizer
and if preserves these coequalizers, then this is equipped with the left -action induced from the left -action on
-
the function module is, if it exists, the equalizer
equipped with the left -action that is induced by the left -action on via
(e.g. Hovey-Shipley-Smith 00, lemma 2.2.2 and lemma 2.2.8)
Proposition
Given a closed symmetric monoidal category (def. , def. ), and given a commutative monoid in (def. ). If all coequalizers exist in , then the tensor product of modules from def. makes the category of modules into a symmetric monoidal category, with tensor unit the object itself, regarded as an -module via prop. .
If moreover all equalizers exist, then this is a closed monoidal category (def. ) with internal hom given by the function modules of def. .
(e.g. Hovey-Shipley-Smith 00, lemma 2.2.2, lemma 2.2.8)
Proof sketch
The associators and braiding for are induced directly from those of and the universal property of coequalizers. That is the tensor unit for follows with the same kind of argument that we give in the proof of example below.
Example
For a monoid (def. ) in a symmetric monoidal category (def. ), the tensor product of modules (def. ) of two free modules (def. ) and always exists and is the free module over the tensor product in of the two generators:
Hence if has all coequalizers, so that the category of modules is a monoidal category (prop. ) then the free module functor (def. ) is a strong monoidal functor (def. )
Proof
It is sufficient to show that the diagram
is a coequalizer diagram (we are notationally suppressing the associators), hence that , hence that the claim holds for and .
To that end, we check the universal property of the coequalizer:
First observe that indeed coequalizes with , since this is just the associativity clause in def. . So for any other morphism with this property, we need to show that there is a unique morphism which makes this diagram commute:
We claim that
where the first morphism is the inverse of the right unitor of .
First to see that this does make the required triangle commute, consider the following pasting composite of commuting diagrams
Here the the top square is the naturality of the right unitor, the middle square commutes by the functoriality of the tensor product and the definition of the product category (def. ), while the commutativity of the bottom square is the assumption that coequalizes with .
Here the right vertical composite is , while, by unitality of , the left vertical composite is the identity on , Hence the diagram says that , which we needed to show.
It remains to see that is the unique morphism with this property for given . For that let be any other morphism with . Then consider the commuting diagram
where the top left triangle is the unitality condition and the two isomorphisms are the right unitor and its inverse. The commutativity of this diagram says that .
Definition
Given a monoidal category of modules as in prop. , then a monoid in (def. ) is called an -algebra.
Propposition
Given a monoidal category of modules in a monoidal category as in prop. , and an -algebra (def. ), then there is an equivalence of categories
between the category of commutative monoids in and the coslice category of commutative monoids in under , hence between commutative -algebras in and commutative monoids in that are equipped with a homomorphism of monoids .
(e.g. EKMM 97, VII lemma 1.3)
Proof
In one direction, consider a -algebra with unit and product . There is the underlying product
By considering a diagram of such coequalizer diagrams with middle vertical morphism , one find that this is a unit for and that is a commutative monoid in .
Then consider the two conditions on the unit . First of all this is an -module homomorphism, which means that
commutes. Moreover it satisfies the unit property
By forgetting the tensor product over , the latter gives
where the top vertical morphisms on the left the canonical coequalizers, which identifies the vertical composites on the right as shown. Hence this may be pasted to the square above, to yield a commuting square
This shows that the unit is a homomorphism of monoids .
Now for the converse direction, assume that and are two commutative monoids in with a monoid homomorphism. Then inherits a left -module structure by
By commutativity and associativity it follows that coequalizes the two induced morphisms . Hence the universal property of the coequalizer gives a factorization through some . This shows that is a commutative -algebra.
Finally one checks that these two constructions are inverses to each other, up to isomorphism.
When thinking of commutative monoids in some tensor category as formal duals to certain spaces, as in def. , then we are interested in forming Cartesian products and more generally fiber products of these spaces. Dually this is given by [fcoproducts] of commutative monoids and commutative -algebras. The following says that these may be computed just as the tensor product of modules:
Proposition
Let be a symmetric monoidal category such that
-
it has reflexive coequalizers
-
which are preserved by the tensor product functors for all objects in .
Then for and two morphisms in the category of commutative monoids in (def. ), the underlying object in of the pushout in coincides with the tensor product in the monoidal category Mod (according to prop. ):
Here and are regarded as equipped with the canonical -module structure induced by the morphisms and , respectively.
This appears for instance as (Johnstone, page 478, cor. 1.1.9).
Remark
In every tensor category (def. ) the conditions in prop. are satisfied.
Proof
By definition, every tensor category is an abelian category (def. ). The coequalizer of two parallel morphisms in an abelian category is isomorphic to the cokernel of the difference (formed in the abelian group struture on the hom-space). Hence all coequalizers exist, in particlar the split coequalizers required in prop. .
Moreover, by definition every tensor category is a rigid monoidal category. This implies that it is also a closed monoidal categories, by prop. , and this means that the functors are left adjoint functors, and such preserve all colimits.
Proposition
Let be a tensor category, and let be a commutative monoid in .
Then for two -algebas according to def. , regarded as affine schemes according to prop. and def. the Cartesian product of with exists in and is the formal dual of the tensor product algebra according to example :
Proof
By prop. the formal dual of the statement is given by prop. , which does apply, according to remark .
Proposition
Let be a symmetric monoidal category, let be two commutative monoids in (def. ) and
a homomorphism commutative monoids (def. ).
Then there is a pair of adjoint functors between the categories of modules (def. )
where
-
the right adjoint, called restriction of scalars, sends an -module to the -module whose action is given by precomposition with :
-
the left adjoint, called extension of scalars sends an -module to the tensor product
(where we are regarding as a commutative monoid in -modules via prop. ) and equipped with the evident action induced by the multiplication in :
Remark
In the dual interpretation of -modules as generalized vector bundles (namely: quasicoherent sheaves) over (def. ) then becomes a map of spaces
and then extension of scalars according to prop. corresponds to the pullback of vector bundles from to .
Super-Groups as super-commutative Hopf algebras
Above we have considered affine spaces (def. ) in symmetric monoidal categories . Now we discuss what it means to equip these with the stucture of group objects, hence to form affine groups in .
A (possibly) familiar example arises in differential geometry, where one considers groups whose underlying set is promoted to a smooth manifold and all whose operations (product, inverses) are smooth functions. These are of course the Lie groups.
A linear representation of a Lie group on a vector space is a smooth function
such that
-
(linearity) for all elements the function
is a linear function
-
(unitality) for the neutral element then is the identity function;
-
(action property) for any two elements, then acting with them consecutively is the same as acting with their product:
But here we need to consider groups with more general geometric structure. The key to the generalization is to regard spaces dually via their algebras of functions.
In the above example, write for the smooth algebra of smooth functions on a smooth manifold . The assignment
is the embedding of smooth manifolds into formal duals of R-algebras from prop. .
Moreover, the functor sends Cartesian products of smooth manifolds to “completed tensor products” of function algebras (namely to the coproduct of smooth algebras, see there)
Together this means that if is equipped with the structure of a group object, then the product operation in the group induces a “coproduct” operation on its smooth algebra of smooth functions:
Now the associativity of the group product translates into a corresponding dual property of its dual, called “co-associativity”, and so forth. The resulting algebraic structure is called a Hopf algebra.
While the explicit definition of a Hopf algebra may look involved at first sight, Hopf algebras are simply formal duals of groups. Since this perspective is straightforward, we may just as well consider it in the generality of groupoids.
A simple illustrative archetype of the following construction of commutative Hopf algebroids from homotopy commutative ring spectra is the following situation:
For a finite set consider
as the (“codiscrete”) groupoid with as objects and precisely one morphism from every object to every other. Hence the composition operation , and the source and target maps are simply projections as shown. The identity morphism (going upwards in the above diagram) is the diagonal.
Then consider the image of this structure under forming the free abelian groups , regarded as commutative rings under pointwise multiplication.
Since
this yields a diagram of homomorphisms of commutative rings of the form
satisfying some obvious conditions. Observe that here
-
the two morphisms are and , respectively, where denotes the unit element in ;
-
the morphism is the multiplication in the ring ;
-
the morphism
is given by .
We now say this again, in generality:
Definition
Let be a tensor category (def. ). A commutative Hopf algebroid in is an internal groupoid in the opposite category of commutative monoids in , regarded with its cartesian monoidal category structure according to prop. .
(e.g. Ravenel 86, def. A1.1.1)
We unwind def. . For , write for same same object, but regarded as an object in .
Proposition
An internal category in is a diagram in of the form
(where the fiber product at the top is over on the left and on the right) such that the pairing defines an associative composition over , unital with respect to . This is an internal groupoid if it is furthemore equipped with a morphism
acting as assigning inverses with respect to .
The key fact to use now is prop. : the tensor product of commutative monoids exhibits the cartesian monoidal category structure on , :
This means that def. is equivalently a diagram in of the form
as well as
and satisfying formally dual conditions, spelled out as def. below. Here
-
are called the left and right unit maps;
-
is called the co-unit;
-
is called the comultiplication;
-
is called the antipode or conjugation
Remark
Generally, in a commutative Hopf algebroid, def. , the two morphisms from remark need not coincide, they make genuinely into a bimodule over , and it is the tensor product of bimodules that appears in remark . But it may happen that they coincide:
An internal groupoid for which the domain and codomain morphisms coincide, , is euqivalently a group object in the slice category over .
Dually, a commutative Hopf algebroid for which and happen to coincide is equivalently a commutative Hopf algebra over .
Writing out the formally dual axioms of an internal groupoid as in remark yields the following equivalent but maybe more explicit definition of commutative Hopf algebroids, def.
Definition
A commutative Hopf algebroid is
-
two commutative rings, and ;
-
ring homomorphisms
-
(left/right unit)
;
-
(comultiplication)
;
-
(counit)
;
-
(conjugation)
-
such that
-
(co-unitality)
-
(identity morphisms respect source and target)
;
-
(identity morphisms are units for composition)
;
-
(composition respects source and target)
-
;
-
-
-
(co-associativity) ;
-
(inverses)
-
(inverting twice is the identity)
;
-
(inversion swaps source and target)
; ;
-
(inverse morphisms are indeed left and right inverses for composition)
the morphisms and induced via the coequalizer property of the tensor product from and , respectively
and
satisfy
and
.
-
e.g. (Ravenel 86, def. A1.1.1)
By internalizing all of the above from to , we obtain the concept of supergroups:
Definition
An affine algebraic supergroup is equivalently
-
a pointed, one-object internal groupoid in the opposite category (def. ) of supercommutative superalgebras from def.
-
the formal dual of a super-commutative Hopf algebra, namely a commutative Hopf algebra (prop. , remark ).
We will often just say “supergroup” for short in the following. If is the corresponding supercommutative Hopf algebra then we also write for this supergroup.
The following asks that the parity involution (def. ) on a supergroup is an inner automorphism:
Definition
An inner parity of a supergroup , def. is an element such that
-
it is involutive i.e.
-
its adjoint action on is the parity involution of def. .
Dually this mean that an inner pariy is an algebra homomorphism such that
-
the composite
is the counit of the Hopf algebra (hence the formal dual of the neutral element)
-
the parity involution conincides with the composite
Example
For an ordinary affine algebraic group, regarded as a supergroup with trivial odd-graded part, then every element in the center defines an inner parity, def. .
Remark
In view of remak , specifying an involutive central element in an ordinary group is a faint shadow of genuine supergroup structure. In fact such pairs are being referred to as “supergroups” in (Müger 06).
Demanding the existence of inner parity is not actually a restriction of the theory:
Example
For any supergroup, def. , and acting on it by parity involution, def. then the semidirect product group has inner parity, def. , given by .
Linear super-representations as Comodules
Definition
Given a commutative Hopf algebroid over (def. ) in some tensor category (def. ), then a left comodule over is
-
an -module object in (def. ) i;
-
an -module homomorphism (co-action)
;
such that
-
(co-unitality)
;
-
(co-action property)
.
A homomorphism between comodules is a homomorphism of underlying -modules making commuting diagrams with the co-action morphism. Write
for the resulting category of (left) comodules over . Analogously there are right comodules.
Example
For a commutative Hopf algebroid, then becomes a left -comodule (def. ) with coaction given by the right unit
Proof
The required co-unitality property is the dual condition in def.
of the fact in def. that identity morphisms respect sources:
The required co-action property is the dual condition
of the fact in def. that composition of morphisms in a groupoid respects sources
Definition
Given two comodules over a commutative Hopf algebra over , then their tensor product is the the tensor product of modules equipped with the following co-action
This is the formal dual of the tensor product of representations, the action on which is induced by
Under the tensor product of co-modules (def. ), these form a symmetric monoidal category (def. ).
Definition
A linear representation of a supergroup , def. , with inner parity , def. , is
- a comodule (def. ) in sVect (def. ) for the formally dual commutative Hopf algebra .
such that
- the inner parity element acts as the identity on and by multiplication with on .
Example
For an ordinary (affine algebraic) group regarded as a supergroup with trivial odd-graded part, and for its neutral element taken as the inner parity, then in the sense of def. is just the ordinary category of representations of .
Proposition
The category of representations of def. of an affine algebraic supergroup , def. , with inner parity (def. ) on finite-dimensional super vector spaces (example ) and equippd with the tensor product of comodules from def. is a -tensor category (def. ) of subexponential growth (def. ).
Moreover, any finite dimensional faithful representation (which always exists, prop.) serves as an -generator (def. ).
See (this prop.).
Super Fiber functors and their automorphism supergroups
The first step in exhibiting a given tensor category as being a category of representations is to exhibit its objects as having an underlying representation space of sorts, and then an action represented on that space. Hence a necessary condition on is that there exists a forgetful functor
to some other tensor category, such that satisfies a list of properties, in particular it should be a symmetric strong monoidal functor.
Such functors are called fiber functors. The idea is that we think of as a bundle over , and over each we find the fiber of that “bundle”, consisting of all those objects in whose underlying object in the given .
The main point of Tannaka duality of tensor categories is the observation that if is a category of representations of some group , then also acts by automorphisms on that fiber functor (i.e. via natural isomorphisms of functors). In good cases then this may be turned around, and the full automorphism group of a fiber functor is identified with the group for which the objects in its fibers are representations, this is the process of Tannaka reconstruction.
There are slight variants on what one requires of a fiber functor. For the present purpose we fix the following definition
Definition
Let and be two -tensor categories (def. ) such that
-
all hom spaces are of finite dimension over .
Let be a commutative monoid (def. ) in the category of ind-objects in (prop. ).
Then a fiber functor on over is a functor
from to the category of module objects over (def. ) in the category of ind-objects (def. ), which is
-
an exact functor in both variables.
If here sVect (def. ), then this is called a super fiber functor.
Definition
A tensor category (def. ) is called
-
a neutral Tannakian category if it admits a fiber functor (def. ) to (example ) (Deligne-Milne 12, def. 2.19)
-
a neutral super Tannakian category if it admits a fiber functor (def. ) to (def. )
-
(not needed here) a general Tannakian category if the stack on which sends to the groupoid of fiber functors to (projective modules over ) is an affine gerbe such that its category of representations is equivalent to (Deligne-Milne 12, def. 3.7).
Given a super fiber functor (def. ) there is an evident notion of its automorphism group: a homomorphism between functors is a natural transformation, and that between monoidal functors is a monoidal natural transformation, according to def. , and this is an automorphism of functors if it is a natural automorphism. We write
for this automorphism group.
So far this is a group without geometric structure (a discrete group). But it is naturally equipped with supergeometry (super-algebraic geometry) exhibited by a rule for what the “geometrically parameterized families” of its elements are. (For exposition of this perspective see at motivation for sheaves, cohomology and higher stacks).
Concretely, this means that for each supercommutative superalgebra with corresponding affine super scheme (def. , def. ) we are to say what the set
of -parameterized elements of is. In fact, under parameter-wise multiplication in the group, any such set must inherit group structure, so that we should have not one discrete group, but a system of them, labeled by supercommutative superalgebras:
Moreover, if is an algebra homomorphism, hence
a map of affine super schemes according to def. , then there should be a group homomorphism
that expresses how a -parameterized family of elements of becomes a -parameterized family, under this map.
For a minimum of consistency, this assignment must be such that the identity map on induces the identity on , and that the composite of two maps of affine superschemes goes to the correspondng composite group homomorphisms.
In conclusion, this says that an algebraic supergeometric structure on is the datum of a presheaf of groups, hence of a functor
such that the underlying points are those of :
Definition
We say that a functor
is representable if there exists a supercommutative Hopf algebra , hence an affine algebraic group (def. ) and a natural isomorphism with the hom functor into :
Definition
Let be a fiber functor (def ).
For a commutative monoid (def. ), write
for its image under extension of scalars along to (prop. ).
With this, the automorphism group of
is defined to be the functor which on objects assigns the discrete group of natural automorphisms of the image of under extension of scalars as above
and which to a homomorphism of algebras
assigns the action of the extension of scalars-functor along :
This is clearly a presheaf, by functoriality of extension of scalars.
Specializing def. to sVect (def. ), where a commutative monoid is a supercommutative superalgebra (def. ) it reads as follows:
Example
Let be a super fiber functor (def ).
For a commutative monoid (def. ), write
For a supercommutative algebra, write
for its image under extension of scalars to (prop. ).
With this, the automorphism super-group of
is defined by
Proposition
For an algebraically closed field of characteristic zero, and for a -tensor category equipped with a super fiber functor , then its automorphism supergroup (def. ) is representable (def. ): there exists a supercommutative Hopf algebra and a natural isomorphism
which, with the Yoneda embedding understood, we write simply as
The following says that in fact all homomorphisms between fiber functors are necessarily isomorphisms:
Lemma
Every monoidal natural transformation (def. ) between two fiber functors (def. ) is an isomorphism (i.e. a natural isomorphism).
(Deligne 90, 8.11 (ii), Deligne 02, lemma 3.2)
Definition
Let be a tensor category and regard the identity functor on it as a fiber functor (def. ). Then the automorphism group of according to def. is called the fundamental group of , denoted:
Example
The fundamental group (def. ) of the category of super vector spaces sVect (def. ) is :
The non-trivial element in acts on any super-vector space as the endomorphism which is the identity on even graded elements, and multiplication by on odd graded elements.
Proposition
For a -tensor category equipped with a super fiber functor (def. ), then the automorphism supergroup of is the image under the super fiber functor of the fundamental group of , according to def. :
Here on the right we are using that is a strong monoidal functor so that it preserves commutative monoids as well as comonoids by prop. , hence preserves commutative Hopf algebras.
Proposition
Let be two -tensor categories and let
be a functor which is -linear, monoidal and exact functor. Then there is induced a canonical group homomorphism
from the fundamental group of (def. ) to the image under of the fundamental group of .
Super-exterior powers and Schur functors
A finite dimensional vector space has the property that a high enough alternating power of it vanishes , namely this is the case for all , and hence this vanishing is just another reflection of the finiteness of the dimension of . For a super vector space of degreewise finite dimension an analog statement is still true, but one needs to form not just alternating powers but also symmetric powers (prop. below), in fact one needs to apply a generalization of both of these constructions, a Schur functor.
The operation of forming symmetric powers and alternating powers makes sense in every tensor category. Moreover, these operations are the two extreme cases of the more general concept of Schur functors: Given any object and given any choice of irreducible representation of the symmetric group , then one consider the subobject of the -fold tensor power that is invariant under this action.
The first step in the proof of the main theorem (theorem below) is the proposition (prop. below) that all objects that have subexponential growth of length (def. ) are actually annihilated by some Schur functor for the symmetric group.
Definition
For a -tensor category as in def., for an object, for and a partition of , regarded as a Young diagram and hence as a representation of the symmetric group , say that the value of the Schur functor on is
where
-
is the subobject of invariants;
-
is the symmetric group on elements;
-
is the irreducible representation of corresponding to ;
-
is diagonal action of on , coming from the canonical permutation action on ;
-
denotes the subspace of invariants under the action
-
the second expression just rewrites the invariants as the image of all elements under group averaging.
Example
For , then equipped with the trivial action of the symmetric group. In this case the corresponding Schur functor (def. ) forms the th symmetric power
For the dual case where then equipped with the action by multiplication with the signature of a permutation and the corresponding Schur functor forms the alternating power
Proposition
Let be a super vector space of degreewise finite dimension . Then there exists a Schur functor (def. ) that annihilates :
Specifically, this is the case precisely if the corresponding Young tableau satifies
Tannaka duality between tensor categories and supergroups
Above we saw that
-
every tensor category equipped with a super fiber functor gives rise to an affine supergroup (prop. );
-
the category of representations of an affine supergroup is a tensor category, prop. .
Indeed, the relation between tensor categories and supergroups is intimate. The following states that under mild size constraints, every tensor category is the category of representations of some affine algebraic supergroup. This shows that the concept of supergroups is fundamental and not accidental.
Theorem
Every -tensor category (def. ) such that
-
is an algebraically closed field of characteristic zero (e.g. the field of complex numbers)
then is a neutral super Tannakian category (def. ) and there exists
-
an affine algebraic supergroup (def. ) whose algebra of functions is a finitely generated -algebra.
-
a tensor-equivalence of categories
between and the category of representations of of finite dimension, according to def. and prop. .
This is due to (Deligne 02, theorem 0.6)
We outline key steps of the proof of theorem , given in Deligne 02. The proof proceeds in three main steps:
-
Proposition states that in a -tensor category an object is of subexponential growth (def. ) precisely if there exists a Schur functor that annihilates it, hence if some power of , skew-symmetrized in sme variables and symmetrized in others, vanishes.
This proposition is where the symmetric group and its permutation action on tensor powers appears, from just a kind of finite-dimensionality assumption.
-
Proposition in turn says that if every object in is annihilated by some Schur functor, then there exists a super fiber functor on over some supercommutative superalgebra , hence then every object of has underlying it a super vector space with some extra structure.
This proposition is where superalgebra proper appears.
-
Proposition states that every -tensor category equipped with a super fiber functor , is equivalent to the category of super-representations of the automorphism supergroup of .
This proposition is the instance of general Tannaka reconstruction applied to the case of fiber functors with values in super vector spaces. This is where the “supersymmetry” supergroup is extracted.
Proposition
For a -tensor category (def. ), then the following are equivalent:
-
for every object there exists and a partition of such that the corresponding value of the Schur functor, def. , on vanishes: .
Proposition
If for every object of a -tensor category (def. ) there exists a Schur functor (def. ) that annihilates it, then there exists a super fiber functor (def. ) over , hence then is a neutral super Tannakian category (def. ).
(Deligne 02, prop. 2.1 “résultat clé de l’article”, together with prop. 4.5)
Proof idea
First (Deligne 02, middle of p. 16) consider the tensor category
which is that of -graded objects of , and whose braiding is given on objects of homogeneous degree by that of multiplied with .
Write and for the tensor unit of , regarded in even degree and in odd degree in , respectively.
For a commutative monoid, write
for the extension of scalars operation , left adjoint to restriction of scalars (prop. ).
Show then that the condition that an object is annihilated by some Schur functor is equivalent to the existence of an algebra such that
for some , hence that each such object is -locally a super vector space.
Moreover, for each short exact sequence
in , there exists an algebra such that
is a split exact sequence, (hence every short exact sequence is locally split).
(Deligne 90, 7.14, Deligne 02, rappel 2.102))
Now (Deligne 02, middle of p. 17) let be the commutative monoid which is the tensor product of commutative monoids (example ) over all isomorphism classes of objects and of short exact sequences in of choices of commutative monoids for which these objects/exact sequencs are locally split, as above.
Then for an -module , write for the subobject of inside .
Check (Deligne 02, bottom of p. 17) that inherits the structure of a commutative monoid, and that inherits the structure of a module over .
Set
Hence for every object , then
has the structure of an -module. By -local splitness of all short exact sequence, is an exact functor.
Hence
is a super fiber functor on over . This restricts to a super fiber functor over on , regarded as the sub-category of even-graded objects in :
Finally check (Deligne 02, prop. 4.5) that if a -tensor category (def. ) admits a super fiber functor (def. ) over a supercommutative superalgebra over
then it also admits a super fiber functor over itself, i.e. a fiber functor to sVect
This is argued by expressing as an inductive limit
over supercommutative superalgebras of finite type over and observing (…) that there exists such that is still a fiber functor and such that there exists an algebra homomorphism .
Finally then the fiber functor in question is
Proposition
For every -tensor category (def. ) and a super fiber functor over (def. )
then induces an equivalence of categories
of with the category of finite dimensional representations, according to def. and prop. , of the automorphism supergroup (example. , prop. ) of the super fiber functor, where is te image of the unique nontrivial element in
This is the main Tannaka reconstruction theorem (Deligne 90, 8.17) specialized to super fiber functors (Deligne 90, 8.19).
References
Monoidal categories were introduced independently by Jean Bénabou and Saunders MacLane under the name ‘categories with multiplication’. The current name is due to Samuel Eilenberg.
-
Jean Bénabou, Catégories avec multiplication , C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris 256 (1963) pp.1887-1890. (gallica)
-
Jean Bénabou, Algèbre élémentaire dans les catégories avec multiplication , C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris 258 (1964) pp.771-774. (gallica)
-
Saunders Mac Lane, Natural Associativity and Commutativity , Rice University Studies 49 (1963) pp.28-46.
Shortly after Mac Lane’s definition appeared, Max Kelly showed how the coherence axioms could be whittled down to just two:
- Max Kelly, On MacLane’s Conditions for Coherence of Natural Associativities, Commutativities, etc. , Journal of Algebra 1 (1964) pp.397-402.
The first monograph:
- Samuel Eilenberg, G. Max Kelly, Closed Categories, pp. 421-562 in: S. Eilenberg, D. K. Harrison, S. MacLane, H. Röhrl (eds.): Proceedings of the Conference on Categorical Algebra - La Jolla 1965, Springer (1966) [doi:10.1007/978-3-642-99902-4]
A more recnt texbook account with emphasis on tensor categories is
-
Pavel Etingof, Shlomo Gelaki, Dmitri Nikshych, Victor Ostrik, chapter 2 of Tensor categories, Mathematical Surveys and Monographs, Volume 205, American Mathematical Society, 2015 (pdf
))
-
Pavel Etingof, Shlomo Gelaki, Dmitri Nikshych, Victor Ostrik, Topics in Lie theory and Tensor categories, Lecture notes (spring 2009) (web)
Commutative algebra internal to symmetric monoidal categories is discussed in
-
Anthony Elmendorf, Igor Kriz, Michael Mandell, Peter May, Rings, modules and algebras in stable homotopy theory, AMS 1997, 2014
-
Mark Hovey, Brooke Shipley, Jeff Smith, Symmetric spectra, J. Amer. Math. Soc. 13 (2000), 149-208 (arXiv:math/9801077)
and specifically for commutative Hopf algebroids in
- Doug Ravenel, chapter 2 and appendix A.1 of Complex cobordism and stable homotopy groups of spheres, 1986 (pdf)
(These authors are motivated by the application of the general theory of algebra in monoidal categories to “higher algebra” (“brave new algebra”) in stable homotopy theory. This is a version of supercommutative superalgebra via example above.)
Free supercommutative superalgebras (Grassmann algebras) were first considered in
Review of basic superalgebra includes
-
Yuri Manin, chapter 3 of Gauge Field Theory and Complex Geometry, Grundlehren der Mathematischen Wissenschaften 289, Springer 1988
-
Dennis Westra, Superrings and supergroups, 2009 (pdf)
Discussion of superalgebras enhanced to smooth algebras (synthetic differential supergeometry) is in
- David Carchedi, Dmitry Roytenberg, On theories of superalgebras of differentiable functions, Theory and Applications of Categories, Vol. 28, 2013, No. 30, pp 1022-1098. (arxiv:1211.6134, TAC)
Deligne's theorem on tensor categories is due to
- Pierre Deligne, Catégorie Tensorielle, Moscow Math. Journal 2 (2002) no. 2, 227-248. (pdf)
building on the general results on Tannakian categories in
- Pierre Deligne, Catégories Tannakiennes, Grothendieck Festschrift, vol. II, Birkhäuser Progress in Math. 87 (1990) pp.111-195. (pdf)
which are reviewed and further generalized in
- Pierre DeligneJames Milne, Tannakian categories, 2012 (pdf)
Surveys are in
-
Victor Ostrik, Tensor categories (after P. Deligne) (arXiv:math/0401347)
The special case of Tannaka duality for ordinary compact groups regarded as supergroups (hence equipped with “inner parity”, def. , just being an involutive central element) is discussed in
- Michael Müger, Abstract Duality Theory for Symmetric Tensor -Categories appendix (pdf), in Hans Halvorson, Algebraic quantum field theory (arXiv:math-ph/0602036), in J. Butterfield & J. Earman (eds.) Handbook of Philosophy and Physics
as a proof of Doplicher-Roberts reconstruction in algebraic quantum field theory.
In their formal dual incarnations as super-graded commutative dg-algebras (super Chevalley-Eilenberg algebras), super L-∞ algebras of finite type had secretly been introduced in
-
Riccardo D'Auria, Pietro Fré Tullio Regge, Graded Lie algebra, cohomology and supergravity, Riv. Nuov. Cim. 3, fasc. 12 (1980) (spire)
-
Peter van Nieuwenhuizen, Free Graded Differential Superalgebras, in Istanbul 1982, Proceedings, Group Theoretical Methods In Physics, 228-247 and CERN Geneva - TH. 3499 (spire)
and hence a whole decade before the explicit appearance of plain (non-super) L-∞ algebras in Lada-Stasheff 92.
The concept was picked up in the D'Auria-Fré formulation of supergravity
- Riccardo D'Auria, Pietro Fré, Geometric Supergravity in D=11 and its hidden supergroup, Nuclear Physics B201 (1982) 101-140 (errata)
and eventually came to be referred to as “FDA”s (short for “free differential algebra”) in the supergravity literature (where in rational homotopy theory one says “semifree dga”, since these dg-algebras are crucially not required to be free as differential algebras).
The relation between super -algebras and the “FDA”s of the supergravity literature is made explicit in
- Domenico Fiorenza, Hisham Sati, Urs Schreiber, Super Lie n-algebra extensions, higher WZW models and super p-branes with tensor multiplet fields International Journal of Geometric Methods in Modern Physics Volume 12, Issue 02 (2015) 1550018, (arXiv:1308.5264)
Last revised on April 27, 2023 at 13:48:20. See the history of this page for a list of all contributions to it.